Chinese Scholars and Overseas Collaborators Make Progress in Health Risk Assessment of Dietary Exposure to Chemicals
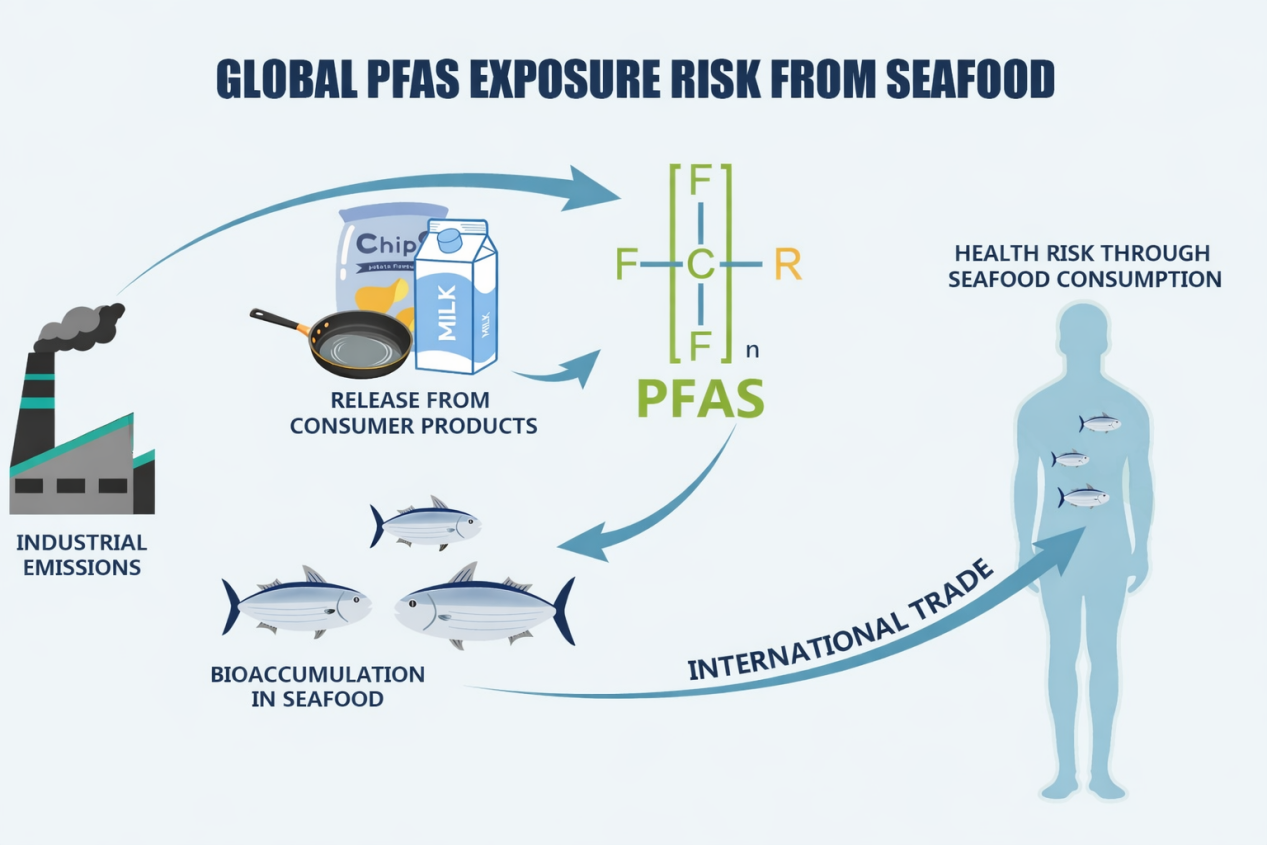
Figure: Conceptual diagram of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances exposure risk through marine fish consumption.
Supported by projects from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.: 42322707, 42222710, 42477297) and others, Associate Professor Wenhui Qiu of Southern University of Science and Technology, Professor Zhaomin Dong of Southeast University, Professor Minghong Wu of Fuzhou University, Professor Chunmiao Zheng of the Eastern Institute of Technology, Ningbo, along with overseas collaborators, have made progress in systematically revealing the global health risks of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances resulting from marine fish consumption. The research findings were published online in the journal Science on December 18, 2025, under the title "Risks of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure Through Marine Fish Consumption." The paper is available at: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adr0351.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a class of artificially synthesized chemicals widely used in industrial production and consumer goods manufacturing. These substances are persistent in the environment, can accumulate through the food chain, and pose potential health threats due to long-term accumulation in the human body. As an important component of the global diet, marine fish may serve as a major source of PFAS intake for humans. However, the contribution of marine fish as a source of PFAS exposure and the associated health risks still lack systematic assessment on a global scale.
The research team integrated environmental concentration data, marine food web models, bioaccumulation factors, global fishing statistics, global trade networks, and health risk assessments to systematically analyze and reveal the PFAS concentrations in 212 species of edible marine fish worldwide and the associated exposure risks from human consumption (Figure). The study found that PFAS exposure levels through marine fish consumption vary among populations in different countries, which is related to economic levels, dietary patterns, and historical PFAS usage; global seafood trade has the potential to reshape PFAS exposure patterns, as PFAS are transferred from high-residue regions to low-residue regions through international seafood trade; and international regulatory policies can effectively reduce PFAS exposure risks; Furthermore, due to their higher persistence and bioconcentration potential, some long-chain PFAS pose more prominent ecological and health risks globally.
This research established an innovative framework, clearly tracing the complete pathway of PFAS from water to marine fish to humans through dietary exposure. It systematically revealed the dynamics of PFAS bioaccumulation in marine food webs and the resulting human exposure risks, clarifying the differences in bioaccumulation among various PFAS homologs and their ultimate risk variations. The findings provide scientific recommendations for fishery managers to develop evidence-based fish consumption guidelines and offer critical data support for improving imported seafood testing standards and optimizing chemical management policies.
Contact Us

National Natural Science Foundation of China
Add: 83 Shuangqing Rd., Haidian District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100085
Tel: 86-10-62327001
Fax: 86-10-62327004
E-mail: bic@nsfc.gov.cn
