Research progress on solar PV power potential along the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and cooperation opportunities among BRI countries
Since the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) was proposed in 2013, the construction of electric power infrastructure has become an important cooperation area, in order to meet future electricity demand and boost regional economic growth. Green BRI construction is becoming a key feature for addressing the challenges of regional sustainable development, as well as global climate change. Solar photovoltaic (PV) power has been the fastest growing renewable energy in recent years. With continuous technological progress and cost reduction, solar PV is expected to play an important role in future low-carbon power transition in the BRI countries.
With the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Excellent Young Scientists Fund, Grant No. 71722003; Major Program, Grant No.71690244), the research team of associate professor Xi LU from the School of Environment, Tsinghua University has carried out fundamental and forward-looking research on the potential and opportunities for solar energy development among BRI countries. The key findings of the analysis are as follows:
(1) The research quantified the solar PV power potential for 66 countries (including China) along the BRI for the first time. The results show that the total annual power generation potential of the BRI region amounts to 448.9 PWh, which is equivalent to 41.3 times the total power demand of the region that occurred in 2016. Tapping that 3.7% of the potential through deploying 7.8 TW capacity could satisfy the regional electricity demand projected for 2030, requiring an investment of approximately 11.2 trillion USD and a commitment in land area of 88,426 km2, approximately 0.9% of China’s total.
(2) The research further revealed the geographic disparity between solar potential and electricity demand. Countries endowed with 70.7% of the overall potential consume only 30.1% of regional electricity. The imbalance underscores the advantage of regional cooperation and investments in regional interconnected grids.
(3) The research found that the utilization of multiple time zones and differentiated weather conditions of the BRI region to transmit complementary solar power will not only meet the overall power demand in the region, but also reduce the impact of solar fluctuations on the electric grid system. This will help break through the technical bottleneck of large-scale application of solar PV generation in the BRI region.
The research was published on August 21, 2019 as a cover paper in Joule, the flagship journal of Cell Press (link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2019.06.006). The analysis has been positively reported by China Daily, Forbes, The Conversation, Yahoo and other media. The research provides new perspectives on jointly developing the regional solar resources of the BRI region at national, industrial and organizational levels, as well as insightful information to the exploration of green and low-carbon development paths for the BRI countries.
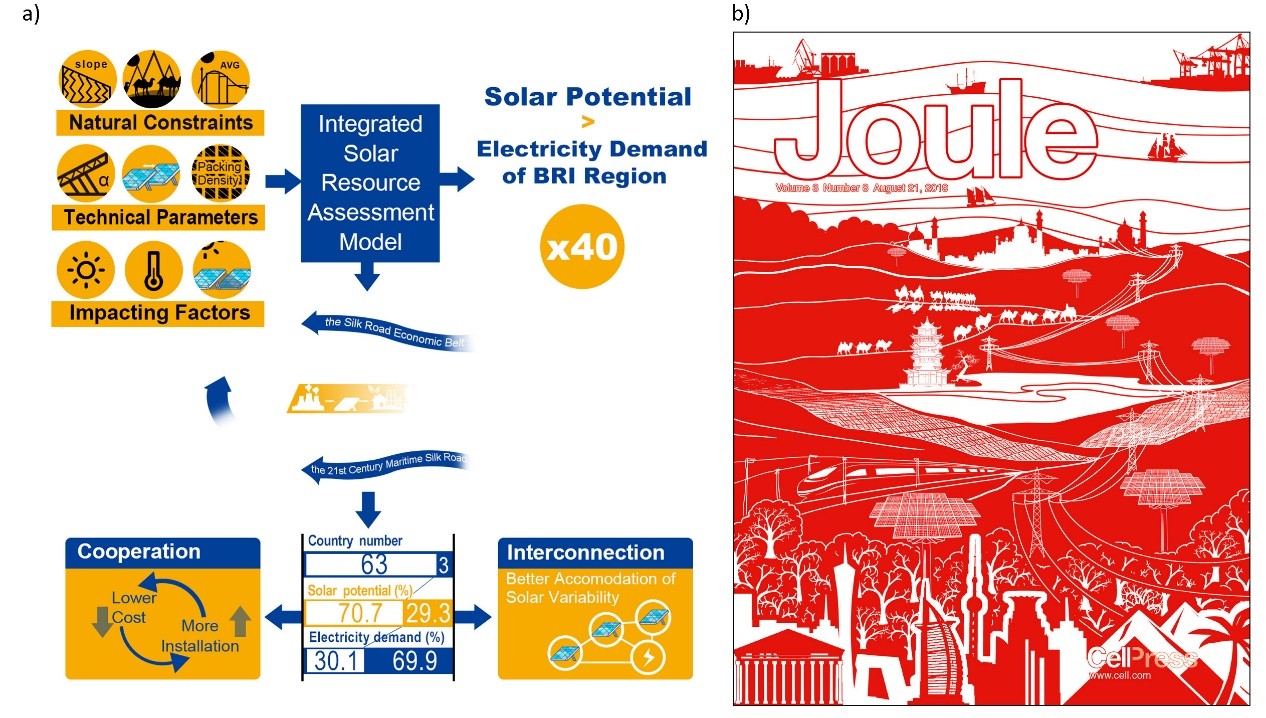
Figure a). Summary of the research; b). Cover of Joule, reflecting the low-carbon and cooperative development of BRI in the form of Chinese paper cutting art
Contact Us

National Natural Science Foundation of China
Add: 83 Shuangqing Rd., Haidian District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100085
Tel: 86-10-62327001
Fax: 86-10-62327004
E-mail: bic@nsfc.gov.cn
